India’s view of the south of the Persian Gulf; Proximity to UAE, Saudi Arabia and Oman

| In recent years, in competition with China, India has increased its economic, political and military presence in the Persian Gulf region, and by improving relations with Saudi Arabia, the UAE and Oman, it has turned itself into an important actor in the Persian Gulf region. |
According to the international group Tasnim News Agency, in recent years, India’s economic relations with the Persian Gulf countries has developed significantly, so that the countries of this region have become the first trading partner of New Delhi. In this context, India’s economic relations with the United Arab Emirates reached 85 billion dollars in 2023, and this country has become India’s third trading partner after the United States and China, and the two countries signed a free trade agreement last year. /p>
India also has extensive economic relations with Saudi Arabia, which, in addition to exporting energy and petrochemicals from Saudi Arabia and exporting goods and sending labor from India, has also seen significant growth in the field of investment. The meeting between the leaders of Riyadh and New Delhi last year led to the conclusion of 20 memorandums of understanding. In this regard, the Saudis are looking for an investment of 100 billion dollars in India, which is the most important joint economic project of the two countries, the Al-Saeed refinery complex on the west coast of India. Is. Currently, the total trade between the two countries is over 5 billion, of which 3 billion are Indian exports and 2 billion are the share of Omani exports. that India and Oman are going to sign a new trade agreement based on which the import tariff for Indian goods in Oman and vice versa will be significantly reduced.
India’s view of the Persian Gulf >
India looks at the Persian Gulf as an economic gateway and a way to reach Europe and therefore seeks to develop economic relations with the countries of the Cooperation Council. Meanwhile, it should be kept in mind that these relations are not only economic and New Delhi is also expanding cooperation with the Persian Gulf countries in the military field. , the development of political and military relations between India and the countries of this region has also been significant. Naval exercises and cooperation agreements and the exchange of military experience of the parties are part of the hidden and unspoken dimensions of this relationship. Meanwhile, China and Pakistan are India’s two rivals in the Persian Gulf region, and they are simultaneously Expanding relations with the countries of the Persian Gulf Cooperation Council. Due to the presence of these two countries in the Persian Gulf equation, security dimensions have been added to India’s presence in the Persian Gulf.
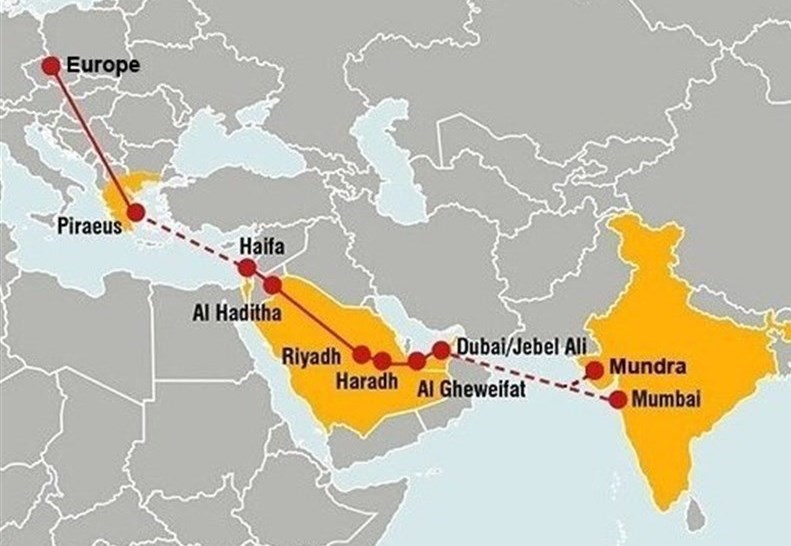
It shows that India’s dependence on the Persian Gulf region has increased significantly, especially after the unveiling of the “Arab-Mod” project.
According to the said plan, Indian goods should go to Saudi Arabia, Jordan and occupied Palestine (Haifa port) via the Persian Gulf (Emirate Port of Fujairah) to be exported to Europe. These conditions have caused the Persian Gulf to become the lifeblood of India and New Delhi, on par with the countries of the subcontinent, shows sensitivity to the developments in the Persian Gulf. Its purpose is to bypass the Strait of Bab al-Mandeb and the Suez Canal and avoid the embargo of the sea route of the Zionist regime by Yemen in support of the oppressed people of Palestine. In order to implement the goals of this corridor, the member countries of this project must pay the cost of loading and unloading several times in the UAE, Saudi Arabia and Haifa port.
This leads to an increase in the cost and time of transporting products. Therefore, experts believe that this project has political and geopolitical goals rather than being economical, to link some countries that interact with Israel to the Zionist regime from another path.
end of message/
| © | Webangah News Hub has translated this news from the source of Tasnim News Agency |